On Oct. 16, 2023 a decision by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission confirmed the ongoing safety of CANDU technology and pressure tubes in Canada’s nuclear reactors.
This decision was informed by years of detailed research and analysis into pressure tube integrity in CANDU reactors and echoes the conclusions of the External Advisory Committee on Pressure Tubes, established by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC), which confirmed in a report earlier this year that “enough has been done by the licensees to definitively provide assurance that the plants can operate safely.”
Read Bruce Power’s full statement here.
If you have any questions or feedback, please fill out the form:
On October 11, 2022 Bruce Power submitted an application to the Commission requesting an amendment of Bruce Power’s Power Reactor Operating Licence to remove Licence Condition 15.3 to reflect the Commission’s latest Records of Decision (DEC 21-H113 and DEC 22-H1001). This request is supported by the advancements in understanding related to pressure tube behaviour and documented satisfaction that pressure tube fracture toughness will be sufficient for safe operation beyond 120 ppm in the regions of interest near the pressure tube inlet and outlet rolled joints.
In 2021, Bruce Power proactively disclosed a technical finding around its pressure tubes to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC).
The finding was identified through robust, planned inspection and analysis activities designed to monitor pressure tube conditions. Hydrogen equivalent concentration (Heq) in some pressure tubes in two units (not operating) were found to be above predicted values and licensing limit.
Since the discovery, Bruce Power expanded outage inspection activities and modified tooling to obtain highly detailed inspection data. These activities have validated the elevated Heq is concentrated to a very small portion of the pressure tube, known as the ‘region of interest.’
Through rigorous processes, Bruce Power concluded there is no impact from the findings on the safety of its units. Putting safety first, Bruce Power completed extensive testing, analysis and evaluations which assessed by the CNSC staff to be compliant with requirements set out in a CNSC Designated Officer Order and the Commission subsequently authorized Bruce Power to restart all units following any outage subject to all other pressure tube fitness for service requirements in the licensing basis being satisfied.
Bruce Power continues to lead industry-level research and development efforts, has shared its operating experience and predictive modeling capabilities with industry peers and keeps the CNSC staff informed of technical advancements related to hydrogen behaviour in pressure tubes in extended operation.
In October 2022, Bruce Power submitted to the Commission an application to amend the licence to formally remove requirement for Commission authorization to operate units with hydrogen concentration measurements >120ppm to reflect the current technical understanding of Heq behaviour. The Commission hearing in writing is in progress
To find out more about pressure tubes and our inspection process, see below. For updates and past news releases, visit our newsroom.
Bruce Power’s Number 1 value has always been ‘Safety First.’ We operate all our units based on this value, and the results of our regular testing program must be conclusive that the fuel channels are safe to operate at all times.
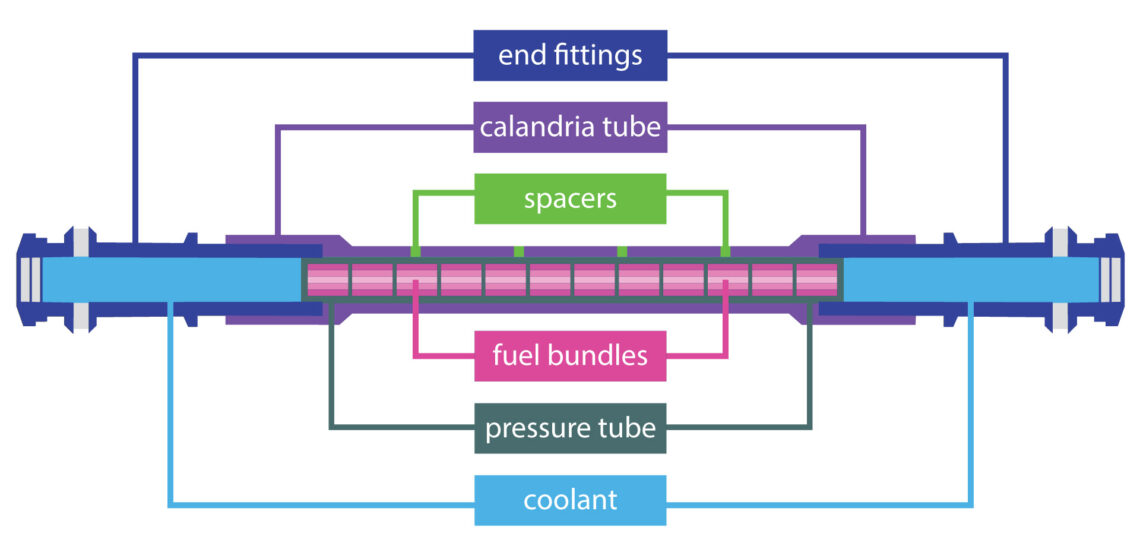
Inside the CANDU reactors at Bruce Power, there are 480 fuel channels. Each fuel channel consists of a pressure tube, a calandria tube, end fittings and spacers.
On the two opposite ends of the pressure tube are end fittings. Inside the pressure tube are the fuel bundles, which generate heat. On the outside of the pressure tube there is the calandria tube, separated from the pressure tube by multiple spacers.
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) licenses nuclear power plant operators, which are required to regularly monitor the condition of pressure tubes to ensure they meet operational fitness standards.
This video describes the function of the fuel channels and pressure tubes, how we test and maintain them, and a description of our innovative Bruce Reactor Inspection Maintenance System (BRIMS) and the tools it delivers to the reactor face.
Fuel Channel Assembly
On the two opposite ends of the pressure tube are end fittings. Inside the pressure tube are the fuel bundles, which generate heat and coolant from the Heat Transport System is used to remove this heat. On the outside of the pressure tube there is the calandria tube, separated from the pressure tube by multiple spacers. Within this gap there is a gas which is measured by an Annulus Gas System (AGS) which measures for moisture and also is a defense in depth measure to ensure integrity of Pressure Tubes.
During regular operation, pressure tubes are exposed to heat, pressure and radiation. Like parts in a car’s engine, these components are tested, maintained and replaced over time. Given the role they play these activities are carried out using many methods.
Through extensive research, testing and modeling development, licensees have a thorough understanding of the impact of aging on pressure tubes. Bruce Power, in cooperation with other CANDU operators and the CANDU Owners Group (COG), has technical experts who are focused on reviewing and analyzing hundreds of data points to confirm the integrity of these components and defense in depth. This work ensures that the pressure tubes continue to meet the required safety margins and that pressure tubes are performing in a predictable manner.
The technical evaluations are updated following each outage and more frequently if new information is obtained from research or regular operational activities that would affect the conclusions of an existing evaluation.
After every inspection campaign, inspected pressure tubes are evaluated against compliance verification criteria to demonstrate that the tube will meet the established safety margins until at least the next planned inspection.
How inspections are carried out
During planned maintenance outages, CANDU reactors all undergo routine testing of fuel channels to test for fitness for duty and safety, measuring factors such as pressure tube and calandria tube changes and elongation; review of fracture protection; in-service considerations; and pressure tube to calandria tube separation.
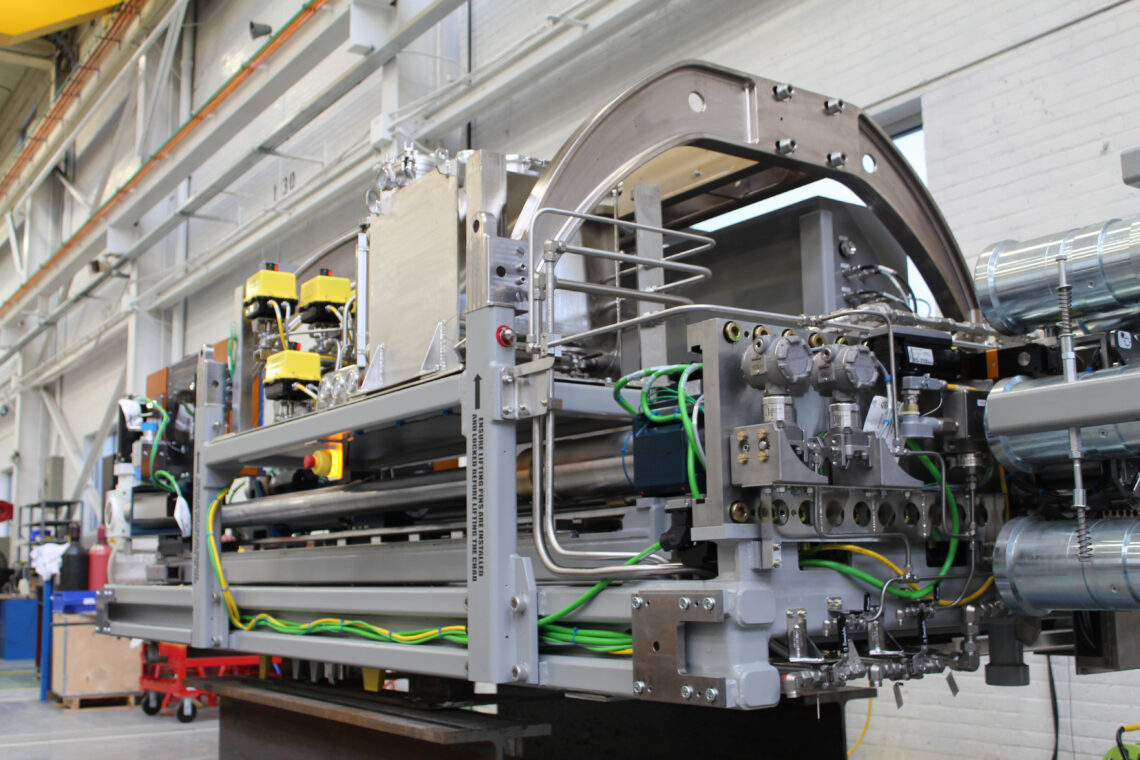
Bruce Power and its partners developed a first-of-a-kind tool that has revolutionized how we conduct this testing. The Bruce Reactor Inspection and Maintenance System (BRIMS) machine is used to deliver our various inspection tools to the reactor face and deploy them into the fuel channels.
Each tool delivered by the BRIMS system is designed to conduct specific and thorough inspections of the fuel channels and pressure tubes. These tools include:
Pressure Tube tools
All of these tools give us a very clear picture of the health of the pressure tubes in our units by providing extremely accurate measurements and data. This large amount of data is also used by Bruce Power technical experts to ensure the integrity of the pressure tubes to achieve safety margins the units continue to operate in a safe and predictable manner.
ANDE – The BRIMS Advanced Non-Destructive Examination (ANDE) tooling system performs ultrasonic inspection in a wet, defueled channel. It takes seven to eight hours to process each channel. This ultrasonic testing measures for flaws, channel diameter, wall thickness, sag, and pressure tube to calandria tube gap, and also locates garter springs. Fundamentally, this is used to verify physical integrity of the tube.

CWEST – The Circumferential Wet Scrape Tool (CWEST) is used to obtain fuel channel metal samples to determine Hydrogen levels inherent in the metal. These metal samples, or scrapes, are taken from various points in the pressure tubes. Fundamentally, this measures hydrogen concentration.
SLAR & MODAR – The Spacer Location and Repositioning Tool (SLAR) and Modal Detection and Reposition (MODAR) detects and repositions garter springs in a wet, de-fueled channel. This ensures adequate separation between calandria and pressure tubes.
How CANDU reactors work
Questions & Answers
Simply put, Effective Full Power Hours on a nuclear reactor is like mileage on a car. Not all miles are equal. It depends on how you operate and maintain the car that determines its lifespan. If you maintain it well and drive it responsibly, the vehicle will last longer. Bruce Power takes great pride in maintaining our nuclear assets through meticulous operation, inspection, maintenance, repair, replacement and monitoring strategies that continue to evolve and improve with technology. Similar to a car, the EFPH calculations take into account when a reactor is at extremely low power (idling), operating at low power (city driving) or operating at full power (highway driving).
300,000 Effective Full Power Hours is written in an abbreviated form as 300 kEFPH. The k is a multiplier by 1,000.
Yes. Bruce Power’s modeling and data demonstrates safe operation to operate to a 300 kEFPH. The CNSC has already reviewed the application and has authorized operation of the Bruce A and B units up to 300 kEFPH in a decision made in 2018.
The original design parameters and length of service for the operational lifespan of a Bruce reactor was a theoretical estimate that was done in the early 80’s before the units came online and started generating power. The estimated lifespan was based on conservative numbers and the best scientific projections at that time. In reality, the reactor components have performed far better than expected and the operational, inspection and metallurgical data supports that. Extensive data for each reactor is collected and updated continuously.
As mandated by the CNSC and part of our operation license, Bruce Power must continuously prove the reactors are safe to operate. Each unit has a planned outage that occurs every two years where extensive inspections and maintenance are performed. During planned outages, detailed measurements and inspections are performed in a sample group of pressure tubes that are selected and approved by the CNSC. The garter springs are located and if required, moved to a more desirable position to prevent contact between the pressure tube and calandria tube. Thin scrape samples of metal from inside of the tubes are sent away for analysis.
Detailed measurements and inspections of the tubes are also performed. Every four years, we are regulated by the CNSC to completely remove and replace one entire fuel channel assembly for extensive testing and end-to-end analysis is completed. Bruce Power collects detailed data on every fuel channel and component. If the data and results are not deemed adequate by the CNSC, the regulator can request more inspections and more data until they are fully satisfied with the results.
The MODAR tool is one of many tools deployed in outages at Bruce Power. It’s used specifically in Unit 8 and is a great example of a unit that would have been shut down if not for advanced tooling. Unit 8 was the last Bruce B unit constructed and came online May 22, 1987. Unit 8 was the first CANDU reactor to use tight fitting garter springs in the fuel channel assembly to help support the pressure tubes (PT) and maintain the gap or space between the PT and calandria tube (CT) to prevent premature degradation of the metal in the PT. During operation, the four spacer springs in each channel tend to gradually move outward towards the ends. The tool used to locate and adjust springs in all units built prior to Unit 8, is a tool known as Spacer Location and Relocation (SLAR). SLAR locates the position of the springs and if required, uses an electromagnetic pulse to move garter springs back toward the center into their desired position. The SLAR tool does not work on tight fitting garter springs. Close to a hundred million dollars and years of development was spent designing, building, and testing a new tool to move the tight-fitting garter springs using harmonics, or vibration. The Modal Detection and Relocation (MODAR) tool was first used in 2015, to shift the location of garter springs in Unit 8 fuel channels to prevent contact between the PT and CTs. It has been used in every Unit 8 planned outage campaign since then for data collection and the movement of springs to maintain safe operational parameters within the core of the reactor.
No, a pressure tube failure is part of the design basis for CANDU reactors, the CANDU design has defense-in-depth systems to maintain control and cooling of the reactor core and prevent any adverse impact on the public. The barriers and systems that protect the reactor and the public from a radiological release include:
- The fuel bundle – The uranium pellets are stacked inside a zirconium sheathed pencil that’s approximately 1 foot in length. 37 pencils are assembled into a bundle format. That outer sheath of the pencil contains the uranium and the radioactive by-products from fission inside this first barrier.
- The pressure boundary system – The pressure boundary system contains the heavy water which flows around the fuel bundles and carries the heat generated up to the steam generators to boil light water which makes steam and turns the turbine generator. The pressure boundary system is considered a barrier as it contains these radioactive elements. Any components that are related to pressure boundary are subject to additional testing rigour and maintenance to ensure it’s integrity. Pressure boundary systems that are connected to the primary heat transport (PHT) or moderator systems are all within a containment structure.
- Negative Pressure Containment – all the reactor vaults, reactor fueling systems, auxiliary heavy water systems and anything connected to PHT or moderator water systems are housed within a protected envelope known as Negative Pressure Containment (NPC). This fortified system keeps any radioactive contamination within its boundaries and the air space inside is maintained at a lower air pressure to ensure any microscopic air incursions will draw clean air in, rather than allowing contamination to escape.
- Emergency Coolant Injection (ECI) – The fuel bundles in the reactor core must be cooled and must be underwater in order for the cooling to be effective. If a LOCA occurred, backup heavy water tanks can inject water into the core to maintain the water in the core. If the backup heavy water tanks were depleted, the ECI system can be triggered to inject cool light water into the core to maintain cooling. The water is collected in the basement of the vault and can be recirculated indefinitely.
- The Vacuum Building – The vacuum building is a large hollow concrete structure designed as the ultimate safety system in the event of a large loss of coolant accident due to a rupture of a feeder tube or main PHT header. In the unlikely event of a major LOCA, steam pressure would rise in the containment structure and the vacuum building would automatically be opened to draw in the steam and any contamination. If the vacuum building was triggered, that also trips a large dousing system of stored cooling water which reduces the heat, volume of steam, and contains the contamination inside the building. The vacuum building must be poised at all times during normal operation and if it is impaired for any reason, the entire station and all 4 units must be shut down if the restoration of this safety system cannot be resolved withing 48 hours.
No. The vacuum buildings have never been activated in emergency response. However, vacuum buildings must also be tested and maintained as per CNSC requirements on a 10-12 year cycle which requires the complete shut-down of all units in the power station.
Yes. Bruce Power has invested millions in the Bruce Units at both stations in response to Fukushima and extreme weather events. In summary, the modifications allow us to use alternate methods to plug in additional cooling, standby power, or filtration. The modifications give us much greater flexibility to cool, contain and control our reactor systems and protect the public in a direct hit of an extreme weather system that damages the existing operational infrastructure.
If you have any additional questions, please contact us through the form at the top of the page, or on our community portal page.






